**谷粒随享**
## 第6章 详情优化
**学习目标:**
- 微服务**分布式链路追踪组件**应用(微服务基础组件)
- 针对于相对高并发业务场景进行性能优化
- 采用分布式缓存Redis
- 缓存击穿(**分布式锁**)
- 缓存穿透(**分布式布隆过滤器**)
- 缓存雪崩(分布式集群)
- 缓存一致性(**基于MySQL-BinLog**数据最终一致)
- 采用异步任务+线程池
- 代码优化:利用AOP将冗余代码抽取-提供自定义缓存注解
# 1、链路追踪Zipkin
一个看起来很简单的应用,背后可能需要数十或数百个服务来支撑,一个请求就要多次服务调用。当请求变慢、或者不能使用时,我们是不知道是哪个后台服务引起的。这时,我们使用 Zipkin 就能解决这个问题。由于业务访问量的增大,业务复杂度增加,以及微服务架构和容器技术的兴起,要对系统进行各种拆分。微服务系统拆分后,我们可以使用 Zipkin 链路,来快速定位追踪有故障的服务点。
**Zipkin/SkyWalking** 是一款开源的分布式实时数据追踪系统(Distributed Tracking System),能够收集服务间调用的时序数据,提供调用链路的追踪。
**Zipkin** 其主要功能是聚集来自各个异构系统的实时监控数据,在微服务架构下,十分方便地用于服务响应延迟等问题的定位。
**Zipkin** 每一个调用链路通过一个 trace id 来串联起来,只要你有一个 trace id ,就能够直接定位到这次调用链路,并且可以根据服务名、标签、响应时间等进行查询,过滤那些耗时比较长的链路节点。
**Zipkin 分布式跟踪系统**就能非常好地解决该问题,**主要解决以下3点问题:**
- 1. 动态展示服务的链路;
- 2. 分析服务链路的瓶颈并对其进行调优;
- 3. 快速进行服务链路的故障发现;
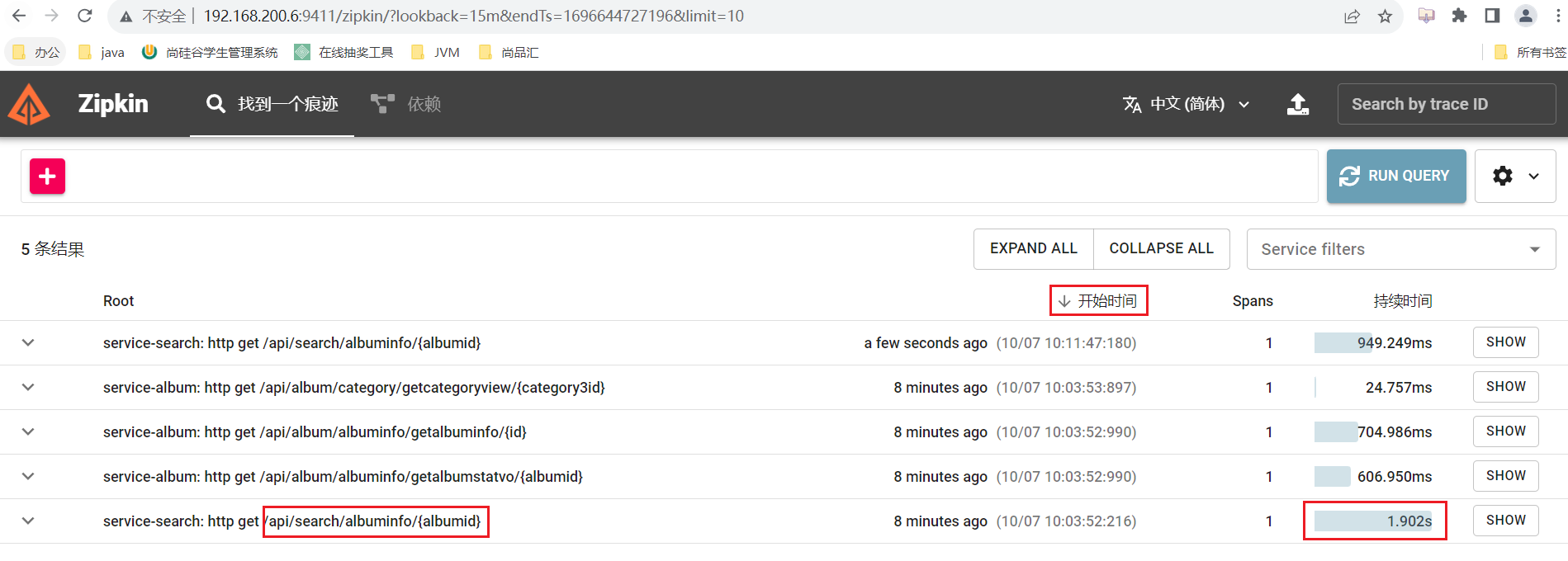
在优化前通过Zipkin链路追踪进行查看接口耗时
1. 在`service-util`工具模块pom.xml中新增Zipkin相关依赖
```xml
io.micrometer
micrometer-tracing-bridge-brave
io.zipkin.reporter2
zipkin-reporter-brave
io.micrometer
micrometer-observation
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-actuator
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-zipkin
2.2.8.RELEASE
io.github.openfeign
feign-micrometer
12.5
```
2. 在Nacos配置`common.yaml`中新增配置(**已完成**)
```yaml
management:
zipkin:
tracing:
endpoint: http://192.168.200.6:9411/api/v2/spans
tracing:
sampling:
probability: 1.0 # 记录速率100%
```
3. 解决异步任务+多线程导致异步Feign请求无法被链路追踪,故需要未线程池设置装饰器(将当前线程内上下文中trace_id传递到子线程中),故将当日资料中复制到`service-util`且设置Spring线程池对象装饰器
```java
//设置解决zipkin链路追踪不完整装饰器对象
taskExecutor.setTaskDecorator(new ZipkinTaskDecorator(zipkinHelper));
```
4. 访问专辑详情接口、或查看专辑页面进行测试
http://localhost:8502/doc.html#/web-api/%E4%B8%93%E8%BE%91%E8%AF%A6%E6%83%85%E7%AE%A1%E7%90%86/getItem
5. 通过Zipkin管理页面查看接口耗时
# 2、详情优化
虽然咱们实现了页面需要的功能,但是考虑到该页面是被用户高频访问的,所以性能需要优化。一般一个系统最大的性能瓶颈,就是数据库的io操作。从数据库入手也是调优性价比最高的切入点。
一般分为两个层面:
- 一是提高数据库sql本身的性能
- 单表
- 全值匹配我最爱、最左前缀要遵守/带头大哥不能死、中间兄弟不能断
- 索引列上少计算、LIKE符号写最右、
- 多表
- 小表(驱动表,在查询条件列上建立索引)驱动大表(被驱动表,关联字段,查询条件,上建立索引)
- 减少子查询,优先使用关联查询
- 关联字段类型一致 、表编码一致
- 二是尽量避免直接查询数据库。
重点要讲的是第二个层面:尽量避免直接查询数据库。
解决办法就是:**分布式缓存**
## 2.1 缓存常见问题
缓存最常见的4个问题:
1. 缓存穿透
2. 缓存雪崩
3. 缓存击穿
4. 缓存一致性
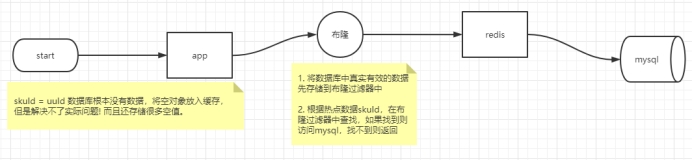
**缓存穿透**: 是指查询一个**不存在的数据**,由于缓存无法命中,将去查询数据库,但是数据库也无此记录,并且出于容错考虑,我们没有将这次查询的null写入缓存,这将导致这个不存在的数据每次请求都要到存储层去查询,失去了缓存的意义。在流量大时,可能DB就挂掉了,要是有人利用不存在的key频繁攻击我们的应用,这就是漏洞。
- 解决1 :空结果也进行缓存,但它的过期时间会很短,最长不超过五分钟,但是不能防止随机穿透。
- 解决2 :使用**布隆过滤器**来解决随机穿透问题。
**缓存雪崩**:是指在我们设置缓存时采用了相同的过期时间,导致缓存在某一时刻同时失效,请求全部转发到DB,DB瞬时压力过重雪崩。
- 解决1:原有的失效时间基础上增加一个随机值,比如1-5分钟随机,这样每一个缓存的过期时间的重复率就会降低,就很难引发集体失效的事件。
- 解决2:如果单节点宕机,可以采用集群部署方式防止雪崩
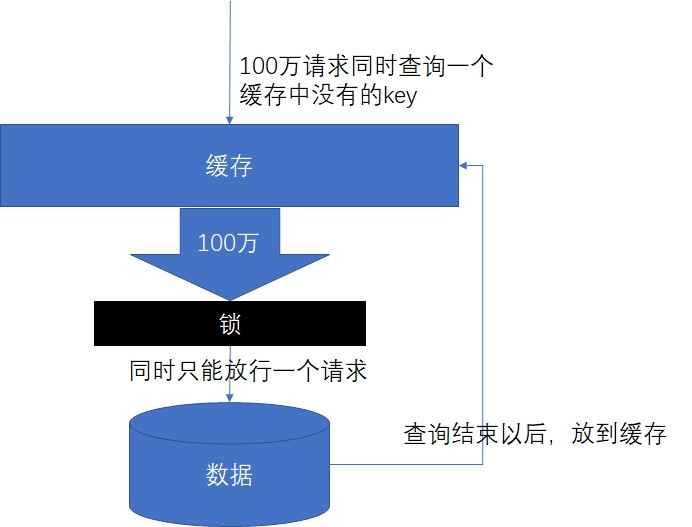
**缓存击穿**: 是指对于一些设置了过期时间的key,如果这些key可能会在某些时间点被超高并发地访问,是一种非常“热点”的数据。这个时候,需要考虑一个问题:如果这个key在大量请求同时进来之前正好失效,那么所有对这个key的数据查询都落到db,我们称为缓存击穿。
与缓存雪崩的区别:
1. 击穿是一个热点key失效
2. 雪崩是很多key集体失效
- 解决:锁
## 2.2 缓存击穿解决方案
### 2.2.1 分布式锁
随着业务发展的需要,原单体单机部署的系统被演化成分布式集群系统后,由于分布式系统多线程、多进程并且分布在不同机器上,这将使原单机部署情况下的并发控制锁策略失效,单纯的Java API并不能提供分布式锁的能力。为了解决这个问题就需要一种**跨JVM的互斥机制**来控制**共享资源**的访问,这就是分布式锁要解决的问题!
分布式锁主流的实现方案:
1. 基于数据库实现分布式锁
2. 基于缓存( Redis等)
3. 基于Zookeeper
每一种分布式锁解决方案都有各自的优缺点:
1. 性能:Redis最高
2. 可靠性:Zookeeper最高(CAP定理-CP)
### 2.2.2 使用 Redisson 解决分布式锁
**Redisson是一个在Redis的基础上实现的Java驻内存数据网格**(In-Memory Data Grid)。它不仅提供了一系列的分布式的Java常用对象,还提供了许多分布式服务。其中包括(BitSet, Set, Multimap, SortedSet, Map, List, Queue, BlockingQueue, Deque, BlockingDeque, Semaphore, Lock, AtomicLong, CountDownLatch, Publish / Subscribe, Bloom filter, Remote service, Spring cache, Executor service, Live Object service, Scheduler service) Redisson提供了使用Redis的最简单和最便捷的方法。Redisson的**宗旨是促进使用者对Redis的关注分离**(Separation of Concern),从而让使用者能够将精力更集中地放在处理业务逻辑上。
官方文档地址:[https://github.com/Redisson/Redisson/wiki](https://github.com/Redisson/Redisson/wiki "https://github.com/Redisson/Redisson/wiki")
实现步骤:
1. 在`service-util` 模块中解开redisson相关依赖(注释放开)
```xml
org.redisson
redisson-spring-boot-starter
```
2. 在`service-util` 模块中添加配置类
```java
package com.atguigu.tingshu.common.config.redis;
import lombok.Data;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.redisson.Redisson;
import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient;
import org.redisson.config.Config;
import org.redisson.config.SingleServerConfig;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* redisson配置信息
*/
@Data
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.data.redis")
public class RedissonConfig {
private String host;
private String password;
private String port;
private int timeout = 3000;
private static String ADDRESS_PREFIX = "redis://";
/**
* 自动装配
*/
@Bean
RedissonClient redissonSingle() {
Config config = new Config();
if (StringUtils.isBlank(host)) {
throw new RuntimeException("host is empty");
}
SingleServerConfig serverConfig = config.useSingleServer()
.setAddress(ADDRESS_PREFIX + this.host + ":" + port)
.setTimeout(this.timeout);
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(this.password)) {
serverConfig.setPassword(this.password);
}
return Redisson.create(config);
}
}
```
3. 优化代码
```java
package com.atguigu.tingshu.album.service.impl;
import com.alibaba.cloud.commons.lang.StringUtils;
import com.atguigu.tingshu.album.service.TestService;
import org.redisson.api.RLock;
import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author atguigu
* @ClassName TestServiceImpl
* @description: TODO
* @date 2023年08月22日
* @version: 1.0
*/
@Service
public class TestServiceImpl implements TestService {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@Override
public void testLock() {
try {
//先尝试获取分布式锁 1.创建锁对象 2.调用获取锁方法
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock("lock");
//获取锁成功后,才执行业务
lock.lock(); //阻塞到获取锁成功为止
//lock.tryLock(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS); //参数1:等待锁获取最大时间 参数2:时间单位 获取锁失败返回false
//lock.tryLock(3, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);//参数1:等待锁获取最大时间 参数2:锁过期时间,参数3:时间单位 获取锁失败返回false
try {
//1.从Redis缓存中获取key="num"的值 保证redis中存在"num"(手动提前在redis中创建key)
String value = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("num");
if (StringUtils.isBlank(value)) {
return;
}
//2.对获取到值进行+1操作
int num = Integer.parseInt(value);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("num", String.valueOf(++num));
} finally {
//业务执行完毕释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
```
分布式锁:
```
ab -n 5000 -c 100 http://192.168.200.1:8500/api/album/test/testLock
```

## 2.3 分布式锁整合业务
```java
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
/**
* 根据专辑ID查询专辑信息(包括专辑标签列表)
* 通过Redisson分布式锁解决缓存击穿问题
*
* @param id 专辑ID
* @return 专辑信息
*/
@Override
public AlbumInfo getAlbumInfo(Long id) {
try {
//1.优先从缓存Redis中获取业务数据
//1.1 构建专辑业务数据Key 形式:前缀+专辑ID
String dataKey = RedisConstant.ALBUM_INFO_PREFIX + id;
//1.2 查询缓存中专辑信息
AlbumInfo albumInfo = (AlbumInfo) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(dataKey);
if (albumInfo != null) {
//2.如果命中缓存,直接返回业务数据即可(不需要查库)
return albumInfo;
}
//3.如果未命中缓存,先获取分布式锁
//3.1 构建当前业务数据锁的Key 形式:业务key+锁的后缀
String lockKey = dataKey + RedisConstant.CACHE_LOCK_SUFFIX;
//3.2 构建当前业务数据锁的对象
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock(lockKey);
//3.3 尝试获取分布式锁 tryLock默认锁过期时间30s底层还有看门狗机制进行锁自动续期
boolean flag = lock.tryLock();
if (flag) {
try {
//4.获取分布锁锁成功,执行查询数据库,并设置缓存
AlbumInfo albumInfoFromDB = this.getAlbumInfoFromDB(id);
int ttl = RandomUtil.randomInt(100, 600);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(dataKey, albumInfoFromDB, RedisConstant.ALBUM_TIMEOUT + ttl, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return albumInfoFromDB;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
//5.释放分布式锁
lock.unlock();
}
} else {
//6.获取分布式锁失败,进行自旋(自旋可能获取锁成功线程会将业务数据已经放入缓存)
return this.getAlbumInfo(id);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("[专辑服务]获取专辑信息锁服务异常异常:{},执行兜底处理方案:{}", e, "直接查询数据库");
return this.getAlbumInfoFromDB(id);
}
}
/**
* 抽取单独查询专辑数据业务方法
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
@Override
public AlbumInfo getAlbumInfoFromDB(Long id) {
//1.根据专辑ID查询专辑信息
AlbumInfo albumInfo = albumInfoMapper.selectById(id);
//TODO 业务校验,校验专辑状态是否为下架状态,只有下架状态专辑才可以被修改
//2.根据专辑ID查询专辑标签列表
LambdaQueryWrapper queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq(AlbumAttributeValue::getAlbumId, id);
List albumAttributeValues = albumAttributeValueMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
if (CollectionUtil.isNotEmpty(albumAttributeValues)) {
albumInfo.setAlbumAttributeValueVoList(albumAttributeValues);
}
return albumInfo;
}
```
## 2.4 AOP与分布式锁整合
专辑详情中多项数据接口需要查询缓存,那么分布式锁的业务逻辑代码就会出现大量的重复。因此,我们可以参考Spring框架事务注解来实现简化代码。只要类上添加了一个注解,那么这个注解就会自带分布式锁的功能。
实现如下:
- 在`service-util` 模块中添加一个注解
- 提供切面类,采用环绕通知对自定义注解进行增强
### 2.4.1 自定义注解
```java
package com.atguigu.tingshu.common.cache;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* 自定义缓存注解
*/
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface GuiGuCache {
/**
* 缓存业务及分布式锁key的前缀
* @return
*/
String prefix() default "data:";
}
```
### 2.4.2 自定义切面类
```java
package com.atguigu.tingshu.common.cache;
import cn.hutool.core.util.RandomUtil;
import com.atguigu.tingshu.common.constant.RedisConstant;
import com.atguigu.tingshu.common.login.GuiGuLogin;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.redisson.api.RLock;
import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
/**
* @author: atguigu
* @create: 2024-08-17 08:57
*/
@Slf4j
@Aspect
@Component
public class GuiGuCacheAspect {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
/**
* 自定义缓存注解的切面逻辑
*
* @param pjp 切入点对象
* @param guiGuCache 方法使用使用注解对象
* @return
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Around("@annotation(guiGuCache)")
public Object doBasicProfiling(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp, GuiGuCache guiGuCache) throws Throwable {
try {
//1.优先从缓存Redis中获取业务数据
//1.1 构建业务数据key 形式=注解前缀+方法参数
//1.1.1 获取注解前缀
String prefix = guiGuCache.prefix();
//1.1.2 获取方法参数如果存在多个参数采用_拼接
String params = "none";
Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();
if (args != null && args.length > 0) {
List